Litepaper
Introduction
Machine learning in a deterministic and permissionless blockchain environment enables the creation and deployment of autonomous smart contract agents. These ML-driven smart contract agents can execute transactions, enforce regulations, introduce optimizations, and make decisions in a decentralized manner, ensuring interoperability with various DApps, DEXs, GameFi, SocialFi, DAOs, and other smart contract applications.
The Adafel Network aims to harness this potential by offering an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) rollup specifically designed for building and deploying ML agents. This whitepaper presents the vision, mission, technological framework, and roadmap of the Adafel Network, detailing how it plans to become the leading platform for decentralized ML solutions.
Vision
Our vision is to create a scalable, efficient, and secure environment where developers and organizations can build, deploy, and manage ML agents seamlessly on the blockchain. Adafel Network aspires to democratize access to advanced ML technologies by leveraging the transparency, security, and decentralization inherent in blockchain systems.
Mission
Adafel Network's mission is to empower developers and organizations by providing a robust, scalable, and customizable EVM rollup optimized for ML workloads. We aim to achieve this by focusing on three core principles:
- Scalability: Ensuring the network can handle the computational demands of ML workloads efficiently.
- Customization: Offering a tailored EVM rollup that supports the unique requirements of ML agents and applications.
- Security and Transparency: Leveraging blockchain technology to provide a secure and transparent environment for ML development and deployment.
Key Features
- Optimized EVM Rollup: A customized EVM rollup designed to efficiently handle ML workloads, offering enhanced performance and scalability.
- Interoperability: Seamless integration with existing Ethereum-based applications and other blockchain networks.
- Decentralized ML Training: Enabling decentralized and collaborative training of ML models, leveraging the computational power of the network.
- On-Chain Inference: Facilitating real-time ML inference on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and security of the results.
- Custom ML Libraries: Providing a suite of ML libraries and tools optimized for on-chain deployment and execution.
Applications
Adafel machine learning (ML) agents can significantly enhance the functionality and efficiency of decentralized applications (DApps) in various ways. Here are some applications:
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Algorithmic Trading: On-chain ML agents can execute trades based on real-time data analysis and predictions, optimizing for maximum returns while managing risks.
- Credit Scoring: These agents can evaluate the creditworthiness of users seeking loans by analyzing on-chain activity and transaction history.
- Risk Management: ML agents can monitor and predict potential vulnerabilities or market crashes, adjusting smart contracts and strategies accordingly.
2. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
- Governance: On-chain ML can analyze voting patterns, predict outcomes, and optimize proposal recommendations to align with the organization's goals.
- Resource Allocation: Agents can dynamically allocate funds and resources based on predictive analytics and member activity.
3. Gaming and Metaverse
- Personalized Gaming Experience: ML agents can analyze player behavior and preferences to offer personalized content, challenges, and rewards.
- In-game Economy Management: They can manage and stabilize the in-game economy by adjusting resource distribution and pricing dynamically based on player interactions.
4. Supply Chain and Logistics
- Predictive Analytics: On-chain ML agents can forecast demand and supply trends, optimizing inventory management and logistics operations.
- Fraud Detection: These agents can identify and prevent fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction patterns and behaviors.
5. Identity and Authentication
- Behavioral Biometrics: ML agents can authenticate users based on their interaction patterns with the DApp, enhancing security.
- Reputation Systems: They can build and maintain reputation scores for users based on their on-chain activities, enabling trustless interactions.
6. Healthcare
- Personalized Medicine: On-chain ML agents can analyze medical records and genetic data to provide personalized treatment recommendations.
- Data Sharing: They can facilitate secure and controlled sharing of health data, ensuring privacy while enabling data-driven insights.
7. Energy Management
- Smart Grids: ML agents can optimize energy distribution and consumption in decentralized energy grids, balancing supply and demand efficiently.
- Carbon Credits: They can manage and verify carbon credit transactions, ensuring transparency and accuracy.
8. Content Creation and Distribution
- Content Recommendation: On-chain ML can analyze user preferences and recommend content (e.g., videos, articles, NFTs) tailored to individual tastes.
- Copyright Protection: They can monitor and enforce copyright policies by analyzing content usage patterns on the blockchain.
9. Insurance
- Automated Claims Processing: ML agents can analyze and verify claims data, automating the claims approval process.
- Risk Assessment: They can predict and assess risks for underwriting purposes, ensuring fair and accurate premium pricing.
10. Environmental Monitoring
- Data Analysis: On-chain ML agents can analyze environmental data (e.g., from IoT devices) to monitor and predict environmental changes.
- Resource Allocation: They can optimize the use of natural resources by predicting shortages and suggesting sustainable practices.
By integrating on-chain ML agents, DApps can become more autonomous, efficient, and capable of handling complex tasks that require real-time data analysis and decision-making.
Why can't we use LLM’s for this?
LLMs are not suitable for big data computations such as machine learning because:
1. Resource Limitations:
- Memory: LLMs run in environments with limited memory, making it challenging to handle large datasets required for big data computations.
- Processing Power: Training machine learning models on big data requires significant computational power, which is beyond the capabilities of typical environments where LLMs operate.
2. Execution Time:
- Complexity and Duration: Training complex machine learning models on large datasets can take hours, days, or even weeks. The execution time in LLM environments is typically constrained, making it impractical to run long-duration computations.
3. Statelessness:
- No Persistent State: LLMs do not maintain state between interactions, meaning they cannot remember or build upon previous computations. Big data tasks often require iterative processing and state persistence, which is not feasible in a stateless environment.
4. Specialized Hardware Requirements:
- GPU/TPU Needs: Efficient big data machine learning computations often require specialized hardware like GPUs or TPUs. LLM environments typically do not provide access to such hardware, limiting their ability to perform intensive computations.
5. Environment Restrictions:
- Sandboxed Execution: LLMs run in a sandboxed environment with restrictions on file access, network communication, and external library usage. Big data computations often rely on accessing large datasets from external sources and using specialized libraries, which may not be supported in a restricted environment.
Competitor Analysis
1. Ritual
- Strengths: Ritual enables the smart contracts to get predictions directly from the offchain models stored in Huggingface or Kaggle. It supports all the mainstream libraries like Tensorflow, Pytorch, etc.
- Weaknesses Currently its an oracle which calls external trusted source for ML predictions and its focus on general purpose models does not contribute much to the Web3 ecosystem.
2. Flock
- Strengths: Flock excels in decentralized AI training and fine-tuning, leveraging federated learning to maintain data privacy while enabling collaborative model development. Its co-creation platform encourages community participation and integrates Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology for enhanced domain-specific AI accuracy
- Weaknesses: While innovative, Flock.io’s focus on federated learning might limit its scalability compared to protocols with more generalized solutions.
3. Ora
- Strengths: Ora is a verifiable LLM oracle built with optimistic ML is a cost-efficient and highly efficient machine learning framework to enable on chain machine learning. It facilitates creation of custom LLM oracle through Initial Model Offering (IMO)
- Weaknesses opML comes at the cost of latency because every request has to wait for a challenge period where multiple validators check for result correctness and hence cannot be used for applications where the response speed is a critical aspect.
4. Galadriel
- Strengths: Galadriel offers a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) setup for calling LLMs and multimodal models, including from closed-source API-providers. Its platform is designed for high customization and deep integration with enterprise systems.
- Weaknesses: The complexity and cost of Galadriel’s solutions might be a barrier for smaller organizations or those with limited technical resources.
Adafel holds a distinct advantage over its competitors due to its innovative integration of machine learning (ML) within the smart contract environment, which is specifically tailored for web3 use cases. This integration brings multiple competitive edges:
-
Direct Integration into Smart Contracts for ML Models: Adafel's ability to seamlessly incorporate ML models directly into smart contracts is a significant advantage. This direct integration allows for real-time data processing and decision-making within the blockchain ecosystem, enhancing the functionality and intelligence of decentralized applications (DApps). Competitors often require additional layers or off-chain processing, which can introduce latency and complexity.
-
Energy and Gas Efficiency: The platform is designed with a focus on energy and gas efficiency. By optimizing the execution of ML workloads within the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) environment, Adafel reduces the computational costs associated with running ML models on-chain. This efficiency not only lowers the cost for users but also makes the platform more sustainable and scalable compared to competitors who may not have optimized their solutions for such efficiency.
-
Interoperability: Adafel emphasizes interoperability, ensuring that its ML agents and smart contracts can interact seamlessly with existing Ethereum-based applications and other blockchain networks. This capability extends the utility of Adafel's solutions across various platforms, making it easier for developers to integrate and leverage Adafel's technology within a broader ecosystem. Competitors that lack such interoperability may face limitations in adoption and integration.
-
Decentralized ML Training and On-Chain Inference: Adafel supports decentralized and collaborative training of ML models, utilizing the network's computational power. This approach democratizes access to ML capabilities and fosters a collaborative environment for model development. Additionally, Adafel's ability to perform on-chain inference ensures that ML predictions and decisions are transparent, secure, and executed within the blockchain's trustless environment. Competitors that rely on centralized or off-chain ML processing may struggle to offer the same level of transparency and security.
-
Custom ML Libraries and Tools: The platform provides a suite of custom ML libraries and tools optimized for on-chain deployment and execution. These tools facilitate the creation of sophisticated ML models that can be efficiently run within the EVM environment. By offering specialized resources for ML development, Adafel simplifies the process for developers and enhances the performance of ML applications. Competitors without such tailored tools may require developers to invest more time and effort in adapting general-purpose ML frameworks for blockchain use.
-
Comprehensive Use Cases: Adafel's whitepaper highlights a broad range of applications for its ML agents, from algorithmic trading and credit scoring in DeFi to governance analysis in DAOs, personalized gaming experiences, and predictive analytics in supply chain management. This versatility demonstrates the platform's potential to revolutionize multiple sectors by making smart contracts more intelligent and adaptive. Competitors that focus on narrower use cases may not be able to address the diverse needs of the blockchain community as effectively.
Technological Framework
1. Adafel Architecture
Adafel is a modular rollup implementing optimizations for the execution of ML workloads within the EVM environment, reducing gas costs and improving performance. The scalable architecture ensures an increase in transaction throughput and decreases latency, ensuring the network can handle large-scale ML applications.
The main components of Adafel comprise:
- Data Layer
- Computation Layer
- ML Application Layer
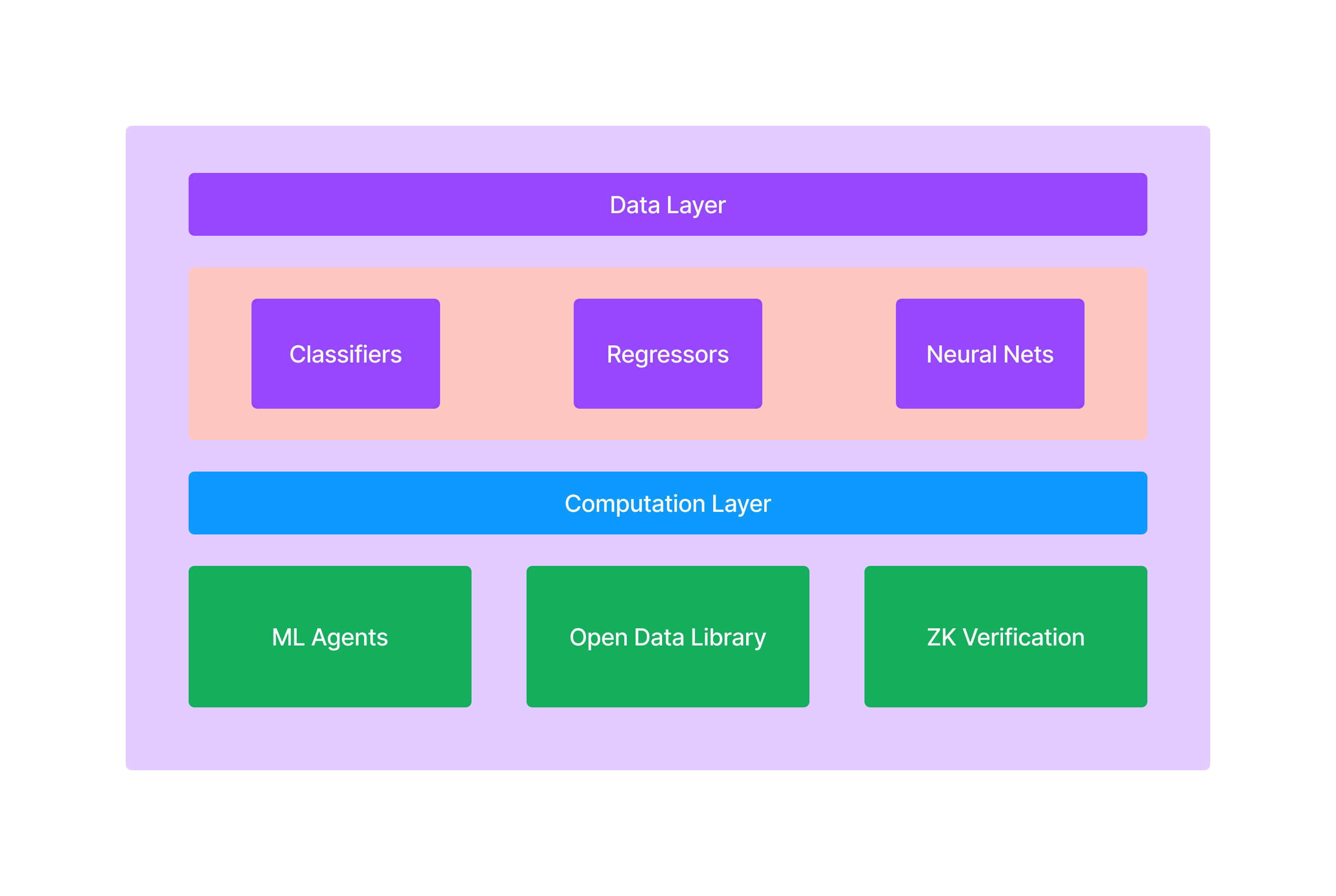
2. Data Layer
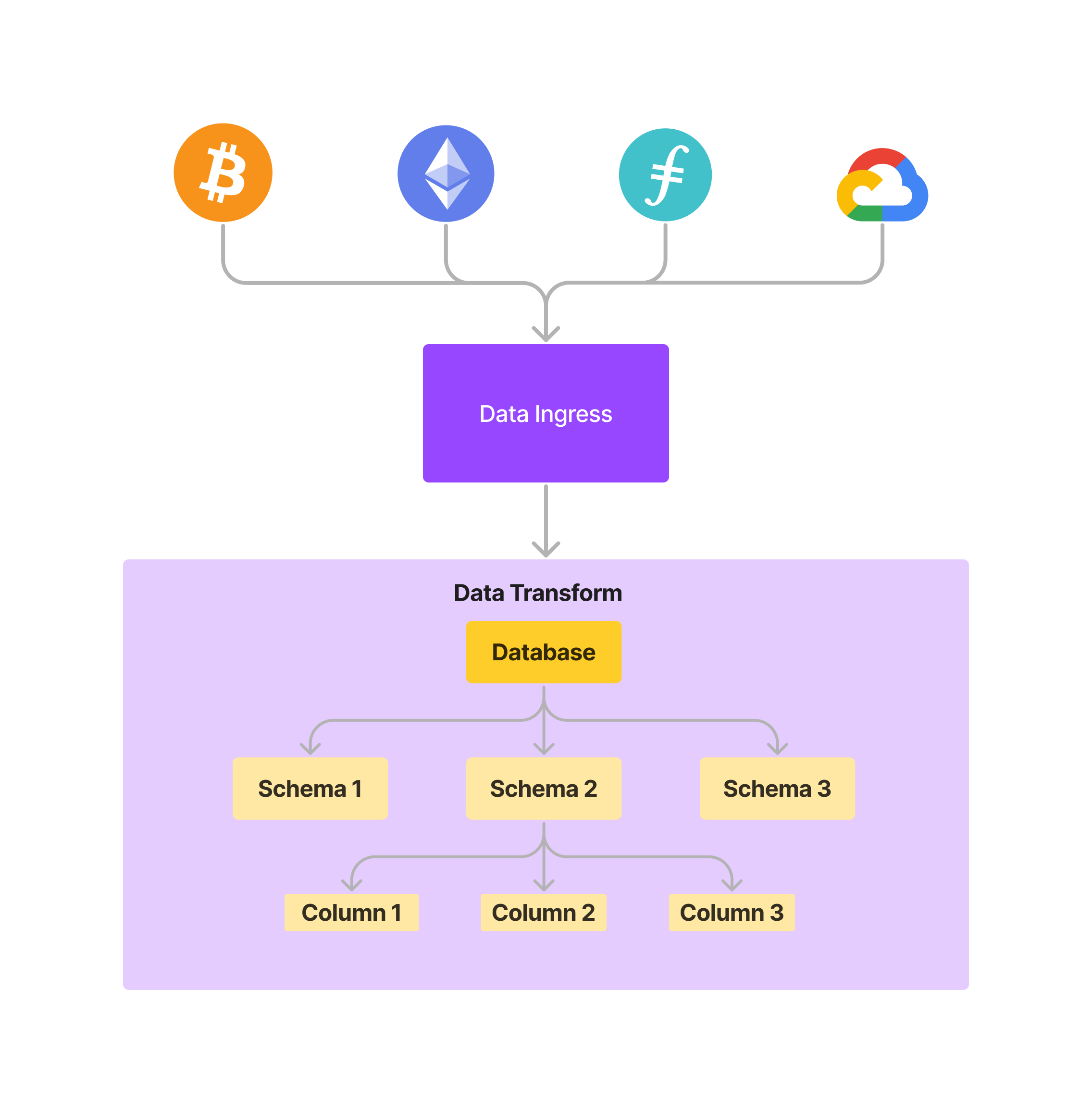
The Adafel data layer is the pipeline for ingestion, extraction, and transformation of data from multiple sources, including Filecoin storage, external Dapps, off-chain cloud storage, and IPFS. This data is then organized into multiple schemas and columns to be consumed by the ML models within the EVM smart contract environment.
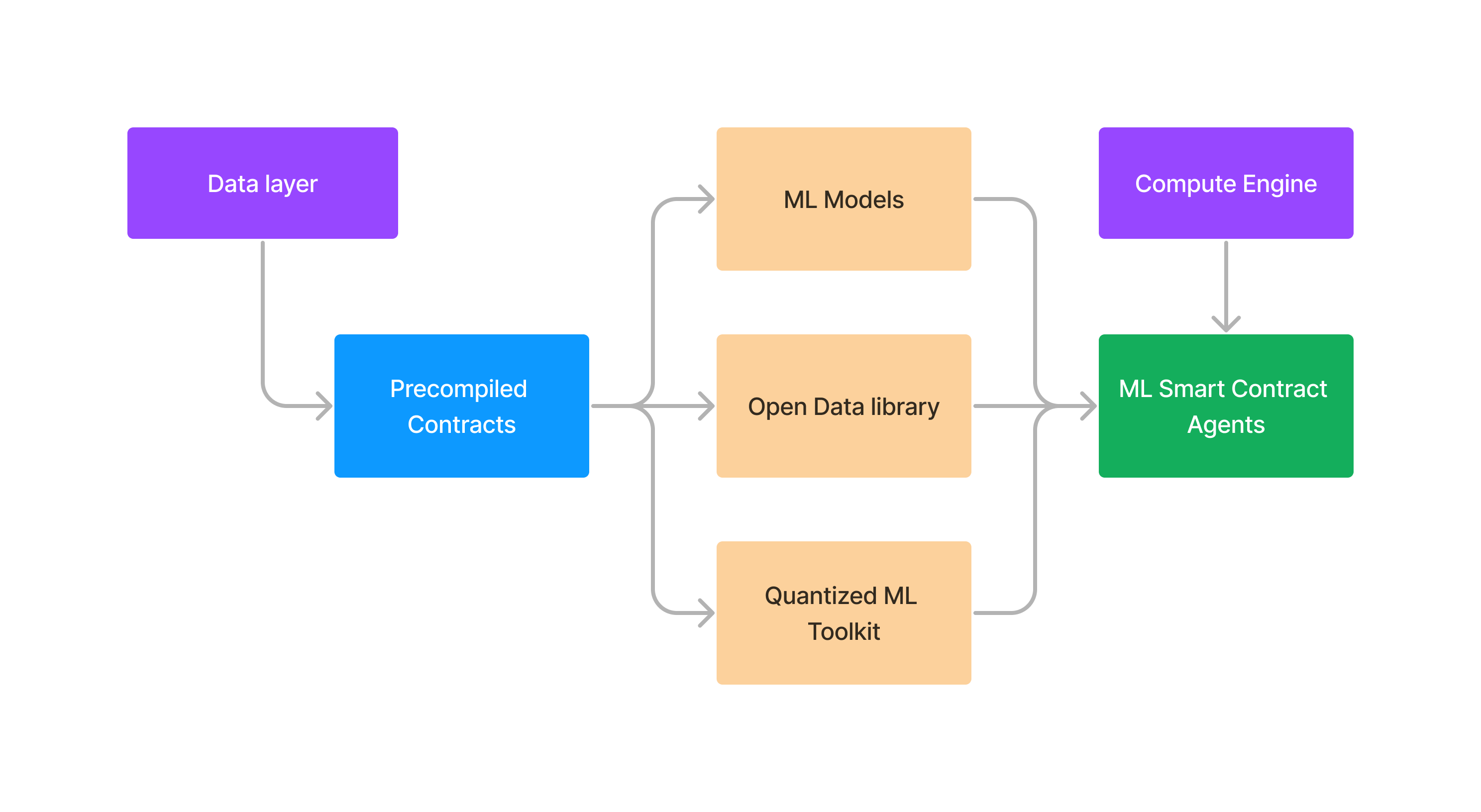
3. Machine Learning Integration
Machine learning is the most computationally intensive operation in the Adafel protocol. To support the demanding tasks of ML training and predictions within the smart contract execution environment, Adafel offers precompiled smart contract toolkits. These toolkits enable the creation of ML classifiers, regressors, neural networks, and quantized ML operations for deterministic predictions. The Open Data Library (ODL) serves as an abstraction layer on top of these precompiled tools, functioning as an SDK for building custom ML models and agents. Additionally, the Adafel EVM compute engine is optimized for decentralized training of ML models, allowing participants to contribute computational resources in a trustless environment.
4. Security and Data Integrity
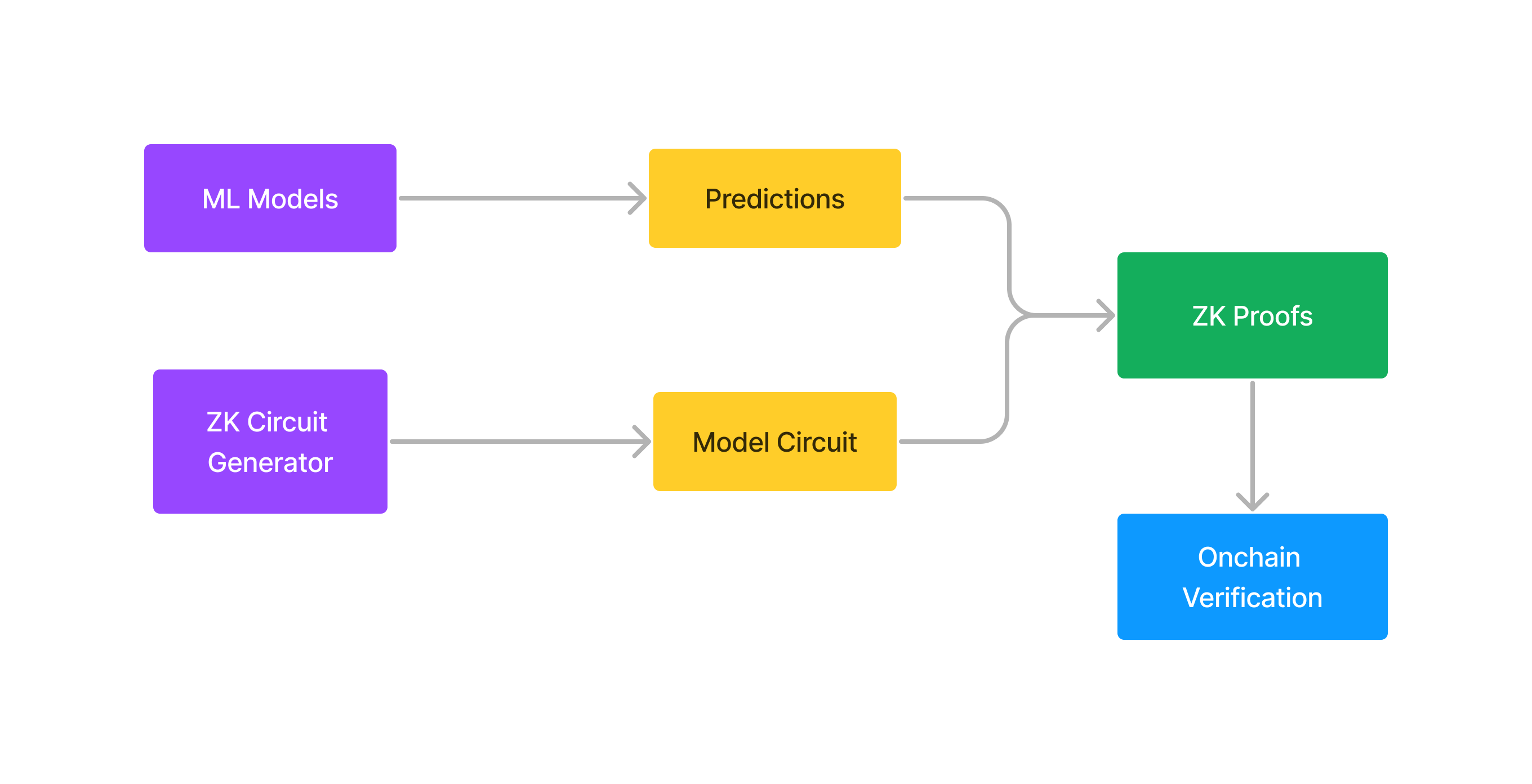
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Leveraging zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) to ensure data integrity during ML training and inference.
- Secure Data Storage: Using decentralized storage solutions like Filecoin to securely store training data and ML models.
5. Interoperability
- Cross-Chain Communication: Implementing interoperability protocols to enable seamless interaction with other blockchain networks, enhancing the utility and reach of ML applications.
- Ethereum Compatibility: Ensuring full compatibility with the Ethereum ecosystem, allowing developers to leverage existing tools and infrastructure.
Tokenomics
The Adafel protocol operates using the $ADFL token for all settlements, with two primary participants:
Data Providers
Data providers include users and DApps that collect and aggregate data for the Adafel protocol. They are incentivized for their contributions. Each data point added to the Adafel protocol data layer earns rewards for the associated address and the DApp sharing its user data. For instance, when transaction data analytics from a DEX is integrated into the Adafel protocol, the addresses involved in the transactions receive $ADFL tokens as rewards, and the DEX is also compensated based on the volume of data provided.
Data Consumers
ML agents consume the aggregated data from various DApps. The $ADFL token is essential for model creation, and DApps wishing to utilize these ML models must stake a minimum amount of $ADFL tokens to access predictions. This staking mechanism ensures commitment and accountability from data consumers.
Roadmap
Phase 1: Network Development
- Design and implementation of the core EVM rollup architecture.
- Development of custom ML libraries and tools.
- Initial testnet launch for early adopters and developers.
Phase 2: Decentralized Training Protocols
- Development and integration of decentralized training protocols.
- Launch of collaborative ML model training features.
- Security audits and optimizations.
Phase 3: Mainnet Launch
- Launch of the Adafel Network mainnet.
- Implementation of on-chain inference capabilities.
- Expansion of interoperability features.
Phase 4: Ecosystem Growth
- Building partnerships with ML and blockchain projects.
- Developing comprehensive documentation and educational resources.
- Ongoing community engagement and support.
Phase 5: Continuous Improvement
- Regular updates and optimizations based on community feedback.
- Introduction of advanced ML capabilities and tools.
- Expansion to support more ML frameworks and blockchain networks.
Team
Adafel Network is founded by a team of experts in blockchain technology, machine learning, and software engineering. Our diverse backgrounds and deep expertise ensure that we can effectively address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by the convergence of these technologies.
Community and Support
We believe that a strong, engaged community is vital to the success of Adafel Network. We are committed to maintaining open lines of communication, actively seeking feedback, and ensuring that our development aligns with the needs and preferences of our users.
Conclusion
Adafel Network is poised to revolutionize the intersection of blockchain and machine learning by providing a scalable, efficient, and secure EVM rollup tailored for ML agents. By leveraging the unique strengths of blockchain technology, we aim
to democratize access to advanced ML capabilities and foster a vibrant, collaborative ecosystem.